5.2.2 Enthalpy and entropy
Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Standard entropy (\(S^\ominus\)) | The entropy of one mole of a substance under standard conditions. Unit \(J \cdot K^{-1} \cdot mol^{-1}\) |
| Entropy (\(S\)) | A measure of the dispersal of energy within the chemicals that make up the chemical system; the greater the entropy, the more disordered a system. Unit \(J \cdot K^{-1} \cdot mol^{-1}\) |
| Free energy change | The balance between enthalpy, entropy and temperature for a process given by \(\Delta G = \Delta H - T\Delta S\). A process is feasible when \(\Delta G < 0\). |
| Feasibility of reaction | Whether a reaction is able to happen and is energetically feasible |
Entropy
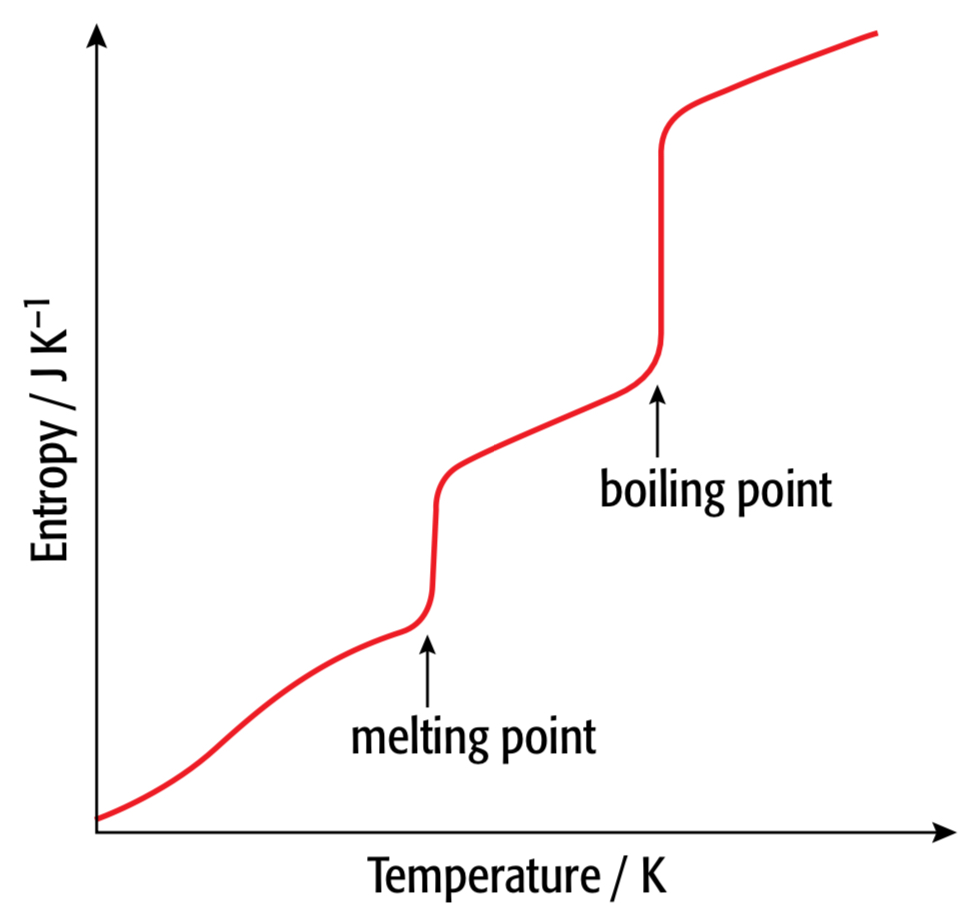
When does entropy increase
- Solid \(\rightarrow\) liquid \(\rightarrow\) gas
- More complex substances with more atoms \(\rightarrow\) simpler substances with fewer atoms
- Increasing the number of molecules (especially gas)
- Increasing the temperature (at 0 K there is no energy and all substances have entropy of 0)
Calculating entropy changes
- \(\Delta S^\ominus = \Sigma S^\ominus (\text{products}) - \Sigma S^\ominus (\text{reactants})\)
Free energy
Free energy change (\(\Delta G\))
- Overall energy change during a chemical reaction
- Made up of enthalpy change (\(\Delta H\)) and entropy change at the temperature of the reaction (\(T\Delta S\))
The Gibbs' equation
- \(\Delta G = \Delta H - T \Delta S\)
- (Note: Convert the unit of \(\Delta S\) to \(kJ \cdot K^{-1} \cdot mol^{-1}\) to match \(\Delta H\))
Gibbs' equation graph
- Graph of \(\Delta G\) against \(T\)
- y-intercept = \(\Delta H\)
- x-intercept = temperature where feasibility changes (\(\Delta G = 0\))
- Gradient = \(-\Delta S\)
Conditions for feasibility
- There must be a decrease in free energy: \(\Delta G < 0\)
- Depends upon enthalpy change (\(\Delta H\)) and entropy change + temperature (\(T\Delta S\))
Limitations or predictions made for feasibility
- Many reactions with \(\Delta G < 0\) don't take place
- \(E_a\) is too high
- The rate is too slow
- Catalysts can be used to overcome the high \(E_a\) so the reaction can take place