5.1.2 How far
Equilibrium
Types of equilibria
- Homogenous equilibria
- Contains equilibrium species that all have the same state or phase
- \(K_c\) contains concentrations of all species
- Heterogenous equilibria
- Contains equilibrium species that all have different states or phases
- \(K_c\) only contains concentrations of gaseous or aqueous species (concentration of solid and liquid is constant)
Equilibrium constant \(K_p\)
Mole fraction
- \(\text{mole fraction } x(A) = \frac{\text{number of moles of A}}{\text{total number of moles in gas mixture}}\)
- (for gases mole fraction can also be calculated by volume of gas divided by total volume)
- Sum of mole fractions = 1
Partial pressure
- The contribution that a gas makes to the total pressure \(P\)
- \(\text{partial pressure } p(A) = x(A) \times P\)
- Sum of partial pressures = total pressure
Changes that affect equilibrium
Effect of temperature change
- When the forward reaction is exothermic
- \(K_c\) or \(K_p\) decreases as the temperature goes up
- \(K_c\) or \(K_p\) increases as the temperature goes down
- When the forward reaction is endothermic
- \(K_c\) or \(K_p\) increases as the temperature goes up
- \(K_c\) or \(K_p\) decreases as the temperature goes down
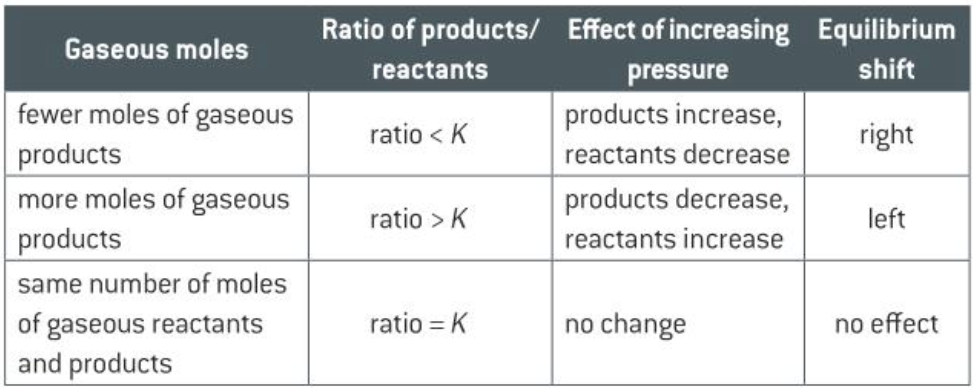
Effect of concentration / pressure change
- The value of \(K_c\) / \(K_p\) stays constant
- e.g. concentration of one of the reactants increase
- The ratio is now less than \(K_c\)
- The system is no longer in equilibrium
- Concentration of products increase + Concentration of reactants decrease to restore ratio
- Total pressure changes
- Partial pressure + ratio change
Effect of catalysts on \(K\)
- Equilibrium reached quicker
- No change in value of \(K_c\) / \(K_p\) or equilibrium position