4.2.4 Analytical technique
Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Fragmentation | The process in mass spectrometry that causes a positive ion to split into smaller pieces, one of which is a positive fragment ion |
| Fragment ions | Ions formed from the breakdown of the molecular ion in a mass spectrometer |
IR spectroscopy
Vibrations in bonds
- Bonds vibrate at a particular frequency
- Stretch: moving along the line between atoms so the distance between them changes
- Bend: results in change in bond angle
- Bonds only absorb radiation with the same frequency as the natural frequency of the bond
- The frequency of the light depends on bond strength, bond length and atomic masses at both ends of the bond
- Most bonds absorb at a frequency of 300 - 4000 \(cm^{-1}\), i.e. IR radiation
- Absorbing IR radiation causes covalent bonds to absorb energy and vibrate more
Greenhouse effect
- Most of the Sun's radiation is short wave and is relatively unaffected by atmospheric gases
- They pass through the atmosphere to the Earth's surface and some is reflected as long wave radiation
- \(C=O\), \(O-H\) and \(C-H\) bonds absorb radiation in the IR range which causes bond in gas molecules to vibrate
- e.g. \(CO_2\), \(H_2O\) and \(CH_4\) molecules
- The vibrating bonds eventually re-emit the energy as radiation that increases the temperature of the atmosphere close to the Earth's surface
- This creates incentives to reduce \(CO_2\) emission to reduce global warming
Infrared spectroscopy
- Determine the functional groups present
- Sample placed in IR spectrometer
- IR radiation beams with wavenumber 200-4000 \(cm^{-1}\) is passed through the sample
- Molecules absorb some IR + emerging beam is analysed to identify frequencies absorbed
- IR spectroscopy is usually connected to a computer that plots a graph of transmittance against wavenumber
- The computer uses the fingerprint region to identify the compound
- Fingerprint region: region below 1500 \(cm^{-1}\) with unique peaks to identify particular molecule
- All organic compounds produce a peak 2850-3100 from \(C-H\) bond
- Look at other peaks to identify other bonds present
Uses of IR spectroscopy in real life
- Remote sensors analyse IR spectra of vehicle emissions to detect pollutants
- IR-based breathalysers pass beams of IR through breathed out gas + detect IR absorbance
- Detecting \(C-O\) bonds in alcohol molecules
- \(O-H\) bond is present in water vapour breathed out so it is not used
- Blood test taken if the result suggests that the person is too drunk to drive safely
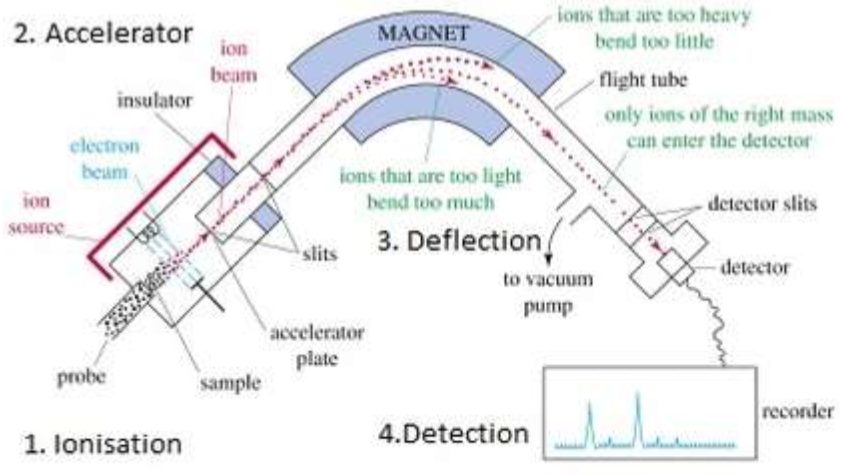
Mass spectroscopy
Mass spectroscopy
- Used to analyse gaseous samples
- Consists of 4 basic regions
- Some molecular ions break down into smaller fragments by fragmentation
Analysing the structure from a mass spectrum
- \(Mr\) = the m/z value of the rightmost peak
- There might be a small peak after M+ peak called the M+1 peak due to the presence of carbon-13 isotope
- Other peaks are due to fragment ions
Common m/z values for fragment ions
| m/z value | Ion (remember to include the + charge) |
|---|---|
| 15 | \(CH_3^+\) |
| 29 | \(CH_3CH_2^+\) |
| 31 | \(CH_2OH^+\) |
| 41 | \(C_3H_5^+, C_2H_3N^+\) |
| 43 | \(CH_3CH_2CH_2^+ / CH_3CO / C_3H_7\) |
| 45 | \(CH_3CH_2O^+\) |
| 49 | \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2^+\) |
- Specify: peak at m/z = ... is due to ...
Combining analytical skills
Identifying the organic compound
- Elemental analysis: empirical formula
- Mass spectrometry: determine molecular mass + identify sections of the molecule
- IR spectrometry: identify bonds + functional groups present