4.1.1 Basic concepts of organic chemistry
Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Functional group | A group of atoms responsible for the characteristic reactions of a compound |
| Homologous series | A series of organic compounds having the same functional group but with each successive member differing by \(CH_2\) |
| Saturated | All carbon to carbon bonds are single bonds |
| Unsaturated | Contain carbon to carbon multiple bonds (\(C=C\) or \(C \equiv C\)) |
| Hydrocarbons | Substances containing carbon and hydrogen atoms only |
| Isomerism | Compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms in space |
| Structural isomers | Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulae |
Basic definitions
Alkyl group
- General formula \(C_nH_{2n+1}\)
- Found on side chains of organic molecules
Types of hydrocarbons
- Aliphatic
- A compound containing carbon and hydrogen joined together in straight chains, branched chains or non-aromatic rings
- Alicyclic
- An aliphatic compound arranged in non-aromatic rings with or without side chains
- Aromatic
- A compound containing a benzene ring
Stem prefix
| Number of carbon atoms | Prefix |
|---|---|
| 1 | Meth- |
| 2 | Eth- |
| 3 | Prop- |
| 4 | But- |
| 5 | Pen- |
| 6 | Hex- |
| 7 | Hept- |
| 8 | Oct- |
| 9 | Non- |
| 10 | Dec- |
Types of formulae
- General formula
- The simplest algebraic formula of a member of a homologous series
- e.g. for an alkane: \(C_nH_{2n+2}\)
- Structural formula
- The minimal detail that shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule
- e.g. for butane: \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_3\) or \(CH_3(CH_2)_2CH_3\)
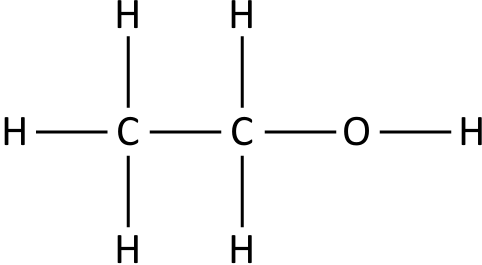
- Displayed formula
- Shows the relative positioning of atoms and the bonds between them
- e.g. for ethanol
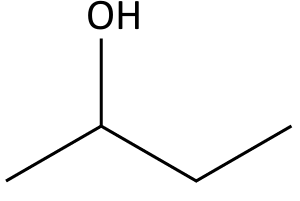
- Skeletal formula
- The simplified organic formula, shown by removing hydrogen atoms from alkyl chains, leaving just a carbon skeleton and associated functional groups
- e.g. for butan-2-ol
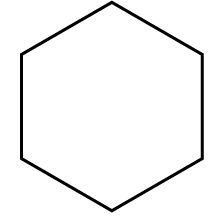
- Cyclohexane
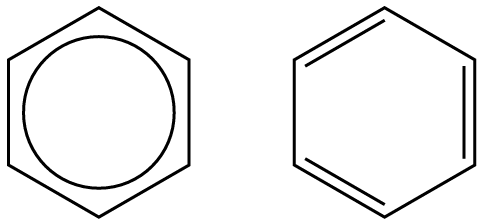
- Benzene
Types of covalent bond fission
- Homolytic fission
- Each bonding atom receiving one electron from the bonded pair forming 2 radicals
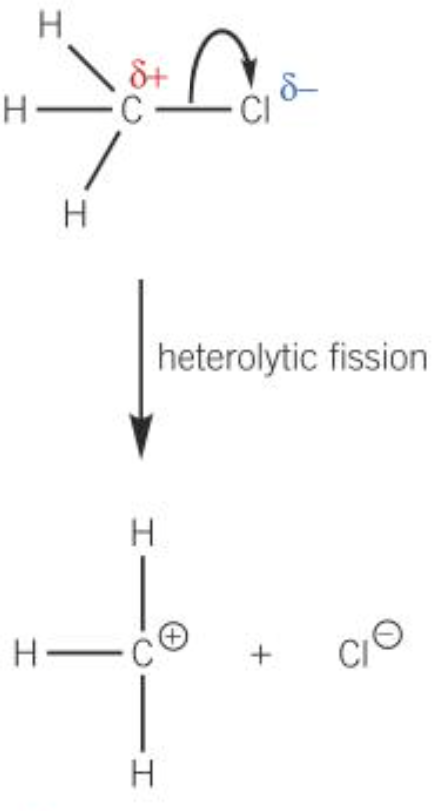
- Heterolytic fission
- One bonding atom receiving both electrons from the bonded pair
- The atom that takes both electrons becomes a negative ion
- The atom that does not take the electrons becomes a positive ion
- e.g. \(H_3C-Cl \rightarrow H_3C^+ + Cl^-\)
Radical
- A species with an unpaired electron
- Represented with a dot (\(\bullet\))
- e.g. \(H_3C-CH_3 \rightarrow H_3C\bullet + \bullet CH_3\)
Curly arrows
- Showing the movement of an electron pair
- Showing either heterolytic fission or formation of a covalent bond
Types of reaction
- Addition reaction
- Two or more reactants join together to form one product
- Substitution reaction
- An atom or group of atoms is replaced by a different atom or group of atoms
- Elimination reaction
- Involves the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
- One reactant molecule forms two products